Our Cutting-edge Technologies
Achieve exceptional precision, and cost-effectiveness, with our laser-based manufacturing technologies
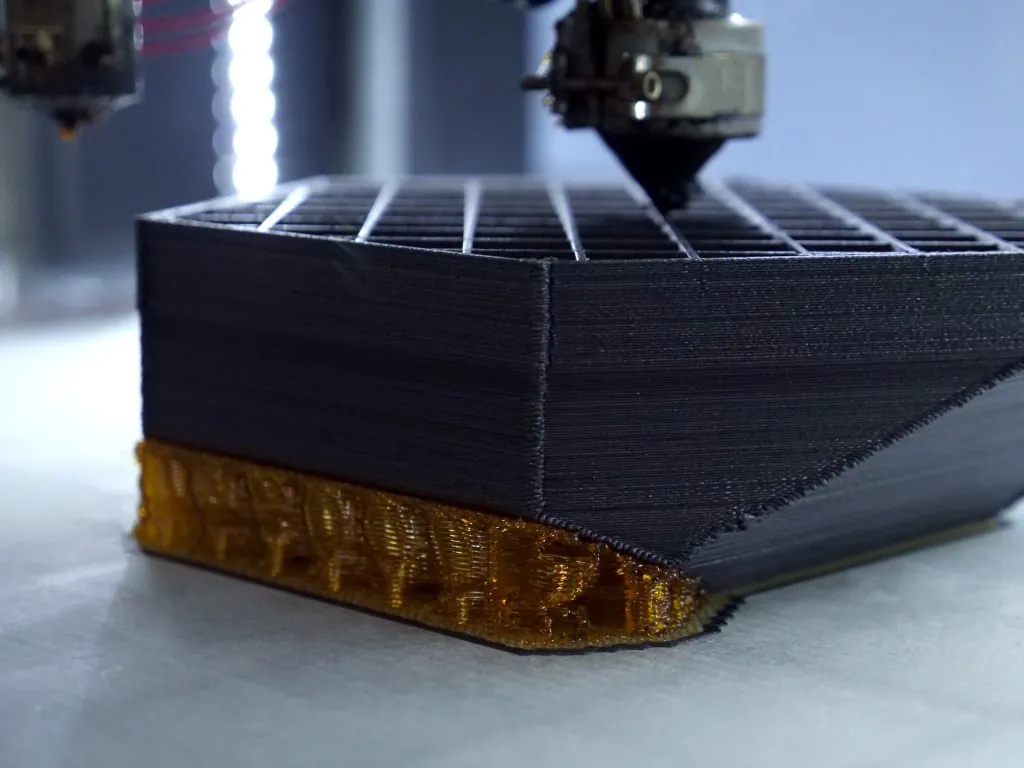
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
Industrial FDM printing uses high-performance thermoplastics to produce strong, precise, and durable parts for demanding industries like aerospace and automotive. It offers superior repeatability, material versatility, and scalability for functional prototypes and end-use components.
- High Strength & Durability
- Consistent & Scalable
- Cost-Effective
- Large & Complex Prints
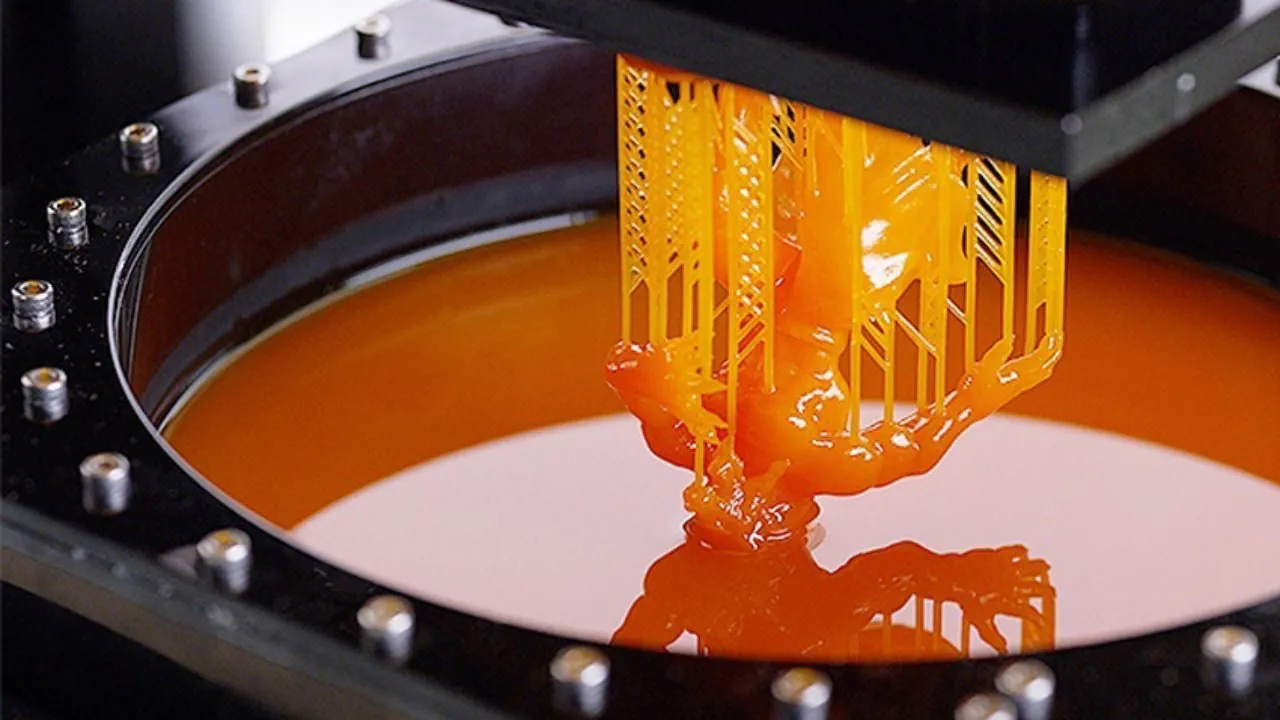
Digital Light Processing (DLP)
Digital Light Processing (DLP) printing uses a digital light projector to cure liquid resin layer by layer, enabling high-speed, high-precision manufacturing. It's ideal for applications requiring fine details, smooth surfaces, and strong mechanical properties, such as dental, jewellery, and engineering industries.
- High Precision & Detail
- Fast Print Speeds
- Strong & Functional Parts
- Smooth Surface Finish